Noncash assets purchased by the trust/estate: 19 based on these authorities, it appears that the only circumstance the irs would allow is to modify an.

As an approach to reduce current income taxes, transfer wealth to family free of gift and estate taxes, and support charitable organizations with regular contributions, charitable lead.
Charitable income tax deductions for trusts and estates. No deduction is allowed for amounts distributed to charities. The limitation is based on the adjusted gross income if paid from unrelated business income. Trusts and estates are not subject to limits on charitable deductions, so long as the payment made to a charitable organization is made out of gross income.
A trust or estate making cash donations may deduct to the extent of the lesser of the taxable income for the year or the amount of the contribution. May be paid from a prior year’s income If the trust or estate allows for payments to be made for charity, then donations from a trust are allowed and may be tax deductions.
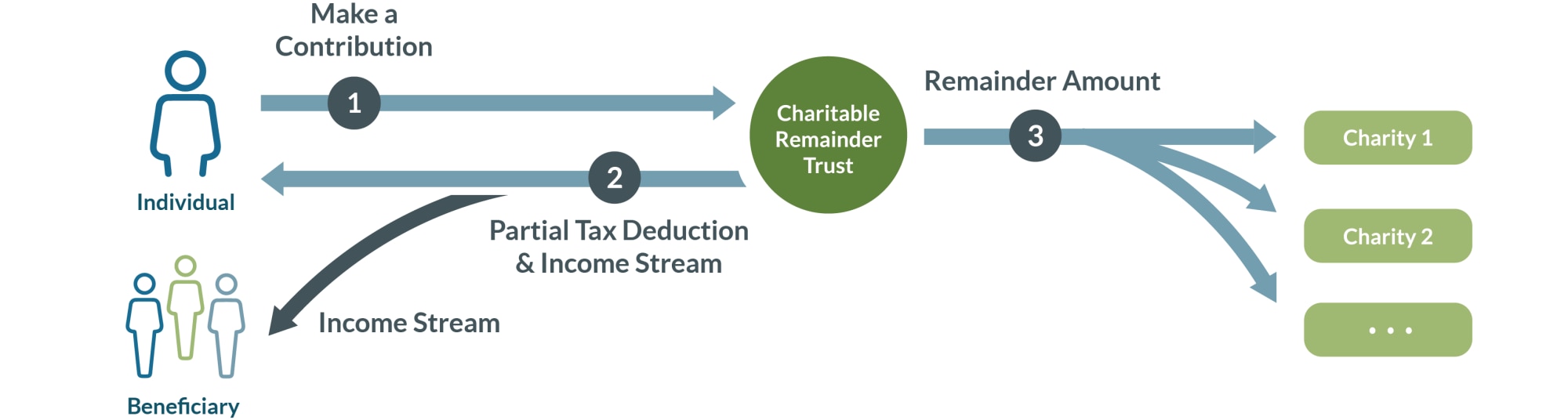
Benefits of charitable distributions from estate or trust income may be paid from gross income of a prior year and the estate may elect to treat a contribution as made for the immediately prior year if paid from gross income of such prior year, if the contribution is paid before filing the return. Another gift that generates annual income is the charitable remainder trust. The irs deducts from that value the amount of income you�re likely to receive from the property.
The value of your gift is not simply the value of the property; For example, when preparing the 2020 form 1041, u.s. The income taxation of trusts and estates, the income taxation of ird, the separate shares of an estate or trust, a specific gift to a charity vs.
The fiduciary may make a $500,000. Charitable gifts of principal are not deductible. While the internal revenue code (irc) does allow estates and trusts an income tax deduction for charitable contributions, wills or trust agreements must contain specific instructions in the document before the testator’s death.
If income is distributed or deemed distributed to the beneficiaries, the trust or estate is allowed a deduction for (all or part of ) the amount of the distribution and the beneficiaries are required to report the amount distributed as their income. Unlike individuals, who are only eligible to take a charitable deduction of up to 50% of adjusted gross income, complex trusts are able to deduct up to 100% of net income for any given year. 2.3.9.1 under the general rule of i.r.c.
Estates and trusts with charitable beneficiaries routinely seek to employ the irs code section 642(c) charitable set aside deduction for income earned by the estate and trust that will eventually (but not in thecurrent tax year) be distributed to the charitable organization.this deduction is needed when the income cannot be currently distributed, since in that case. As an approach to reduce current income taxes, transfer wealth to family free of gift and estate taxes, and support charitable organizations with regular contributions, charitable lead. For both trusts and estates, the charitable contribution is deductible only to the extent that the amount donated was paid or set aside from income.
Section 642(c) unlimited deduction but requirements (paid, or for estates also set aside, from gross income, pursuant to the terms of the governing instrument, for a charitable purpose, no us requirement). If the trust or estate has taxable income in a given year, the fiduciary may elect to treat charitable distributions made in the subsequent year as paid in the first year. However, charitable contributions made by trusts are treated differently under the internal revenue code from those made by other taxpayers.
For trusts created on or before october 9, 1969, the irs code expands the scope of the deduction to allow for a deduction of the gross income set aside permanently for charitable purposes. 642 (c) (1), estates and trusts both are entitled to charitable deductions for “any amount of the gross income, without limitation, which pursuant to the terms of the governing instrument is, during the taxable year, paid” to a charity. Trusts & estates trusts and estates:
If the charitable lead trust is funded with a donation of cash, the donor can claim a deduction of up to 60% of. Income tax return for estates and trusts, a fiduciary discovers a trust has $500,000 of taxable income. 19 based on these authorities, it appears that the only circumstance the irs would allow is to modify an.
Like individuals and corporations, trusts and estates that make contributions of property to charitable organizations may be eligible to receive a corresponding income tax deduction for such. Trust and estate attorneys must have a complete understanding of these rules and reporting requirements for claiming charitable. Charitable contributions must be paid out of the trust’s gross income and not the underlying principal of the trust.
If income is not distributed but instead accumulated, it is taxed to the trust or estate. Income tax you can take an income tax deduction, spread over five years, for the value of your gift to the charity. Gross income must be included in taxable incomein order to allow for the deduction, and therefore is not allowed for:
If an element is omitted, the amount donated to charity is not deductible. Terrible trouble certainly awaits the assumptive charitable testator. In two separate chief counsel advice materials, the irs has ruled that modifying a trust to include authority to make charitable contributions does not qualify the trust to take a charitable income tax deduction when the original trust did not give that authority.
Irc section 642 (c) governs income tax charitable deductions for trusts and estates, which are substantially different from charitable contribution deductions for individuals and corporations under sec. Like individuals and corporations, trusts and estates that make contributions of property to charitable organizations may be eligible to receive a corresponding income tax deduction for such contributions. The authors have discussed the many legal topics invoked in answering when can an estate or trust distribute ird to a charity and receive an income tax charitable deduction:
If the trust or estate purchased marketable securities with income, the cost basis of the asset is considered the amount contributed from gross income. Where things get tricky is determining the amount of your deduction. Donate cash or appreciated property to the trust.
Depending on the structure, the donor can benefit from a stream of income during the life of the trust, deductions for gift and estate taxes, as well as current year income tax deductions when the assets are donated to the trust. Noncash assets purchased by the trust/estate: